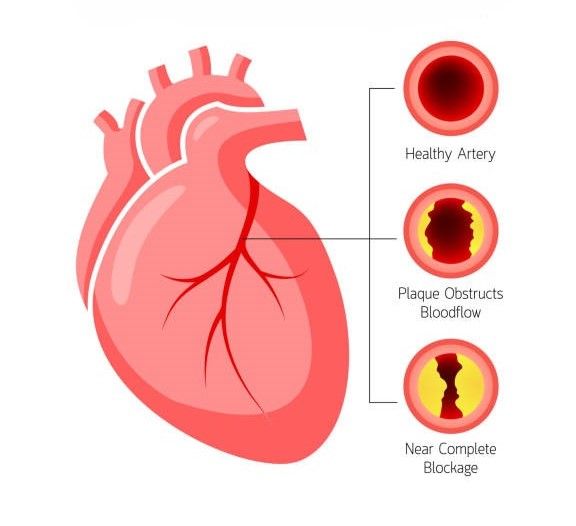
What Causes It?
Buildup of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) - The most common cause of CAD is atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up inside the arteries.
Damage to the inner layer of coronary arteries - This can be caused by various factors including smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or insulin resistance.
Inflammation - Chronic inflammation in the arterial walls can lead to the buildup of plaque.
Genetic factors - Family history plays a significant role in the development of CAD.
Lifestyle factors - Lack of exercise, poor diet, obesity, and stress can contribute to the development of CAD.
Signs & Symptoms
Chest pain (angina) - You may feel pressure or tightness in your chest, as if someone were standing on your chest.
Shortness of breath - If your heart can't pump enough blood to meet your body's needs, you may develop shortness of breath or extreme fatigue with activity.
Heart attack - A completely blocked coronary artery will cause a heart attack. The classic signs and symptoms of a heart attack include crushing pressure in your chest and pain in your shoulder or arm, sometimes with shortness of breath and sweating.
Fatigue - Feeling more tired than usual and having less energy may be symptoms of heart disease, especially in women.
Nausea and dizziness - These symptoms may occur during activity or times of stress, particularly if your heart isn't functioning properly.
Irregular heartbeat - Changes in your heart's rhythm may be a sign of heart disease.