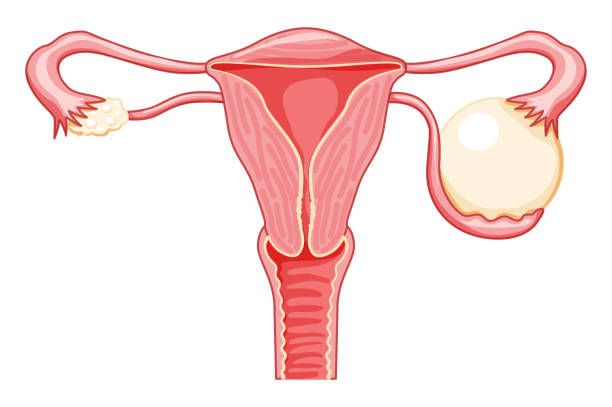
What Causes It?
Normal menstrual cycle function - The most common type of ovarian cysts (functional cysts) form during the menstrual cycle. Follicular cysts occur when the follicle that normally releases an egg doesn't open, and corpus luteum cysts form when the follicle seals after releasing the egg and fills with fluid.
Endometriosis - When tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, it can attach to the ovary and form a growth (endometrioma).
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) - This hormonal disorder causes the ovaries to enlarge with multiple small cysts.
Pregnancy - The corpus luteum, which produces hormones to support pregnancy until the placenta forms, can sometimes fill with fluid and form a cyst.
Pelvic infections - Severe pelvic infections can spread to the ovaries and fallopian tubes, causing cysts to form.
Previous ovarian cysts - Having had ovarian cysts increases the likelihood of developing more.
Hormonal imbalances - Conditions that affect hormone levels can increase the risk of developing ovarian cysts.
Early menstruation or menopause - Starting menstruation at an early age or experiencing menopause late may increase risk.
Smoking - Some research suggests smoking may increase the risk of certain types of functional ovarian cysts.
Fertility treatments - Medications used to induce ovulation can sometimes lead to the development of multiple follicular cysts.
Signs & Symptoms
No symptoms - Many ovarian cysts cause no symptoms and are discovered during pelvic examinations or imaging studies done for other reasons.
Pelvic pain - Ranging from dull and aching to sharp and severe, often on the side of the cyst.
Abdominal bloating or swelling - Particularly with larger cysts.
Pain during intercourse - Discomfort during sex, especially with deep penetration.
Pain during bowel movements or urination - When cysts press on the bladder or rectum.
Irregular menstrual periods - Changes in cycle length, timing, or intensity.
Abnormal bleeding - Including spotting or bleeding between periods.
Breast tenderness - Due to hormonal changes related to the cyst.
Nausea and vomiting - Particularly if a cyst is twisting (torsion) or rupturing.
Fullness or heaviness in the abdomen - Especially with larger cysts.
Pressure on the bladder or rectum - Leading to frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder completely.
Sudden, severe pain - Which may indicate cyst rupture, torsion, or bleeding within a cyst, requiring immediate medical attention.