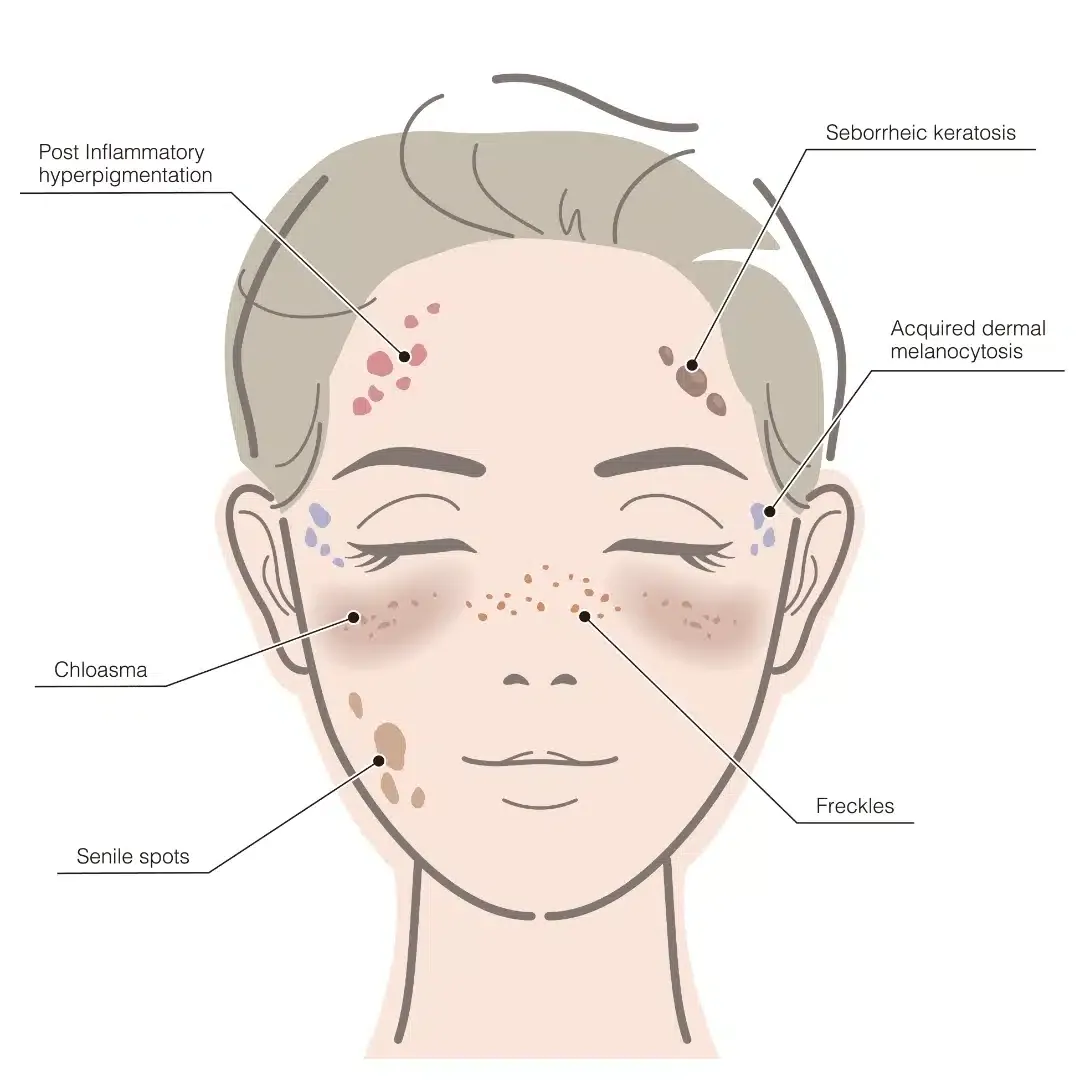
What Causes It?
Acne lesions (most common)
Eczema, psoriasis, insect bites
Laser treatments or chemical peels (overdone)
Cuts, burns, or friction injuries
Excessive picking or squeezing pimples
Allergic skin reactions or irritants
Signs & Symptoms
Flat, darkened patches or spots on the skin
Brown, black, red, or purple discoloration (based on skin tone and depth)
Commonly seen on the face, back, shoulders, chest, or areas of injury
No pain, itching, or texture change — purely a pigmentation issue