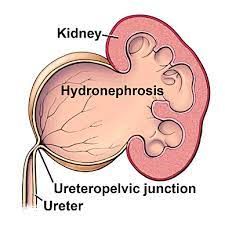
What Causes It?
Congenital Narrowing – Developmental defect where the UPJ is abnormally narrow from birth.
Compression by Blood Vessels – Nearby arteries may press against the UPJ.
Scar Tissue – Due to previous urinary tract surgeries or infections.
Kidney Stones – Large stones blocking the UPJ.
Tumors – Rare growths pressing on the urinary pathway.
Infection-related Swelling – Severe UTIs causing tissue inflammation.
Post-traumatic Injury – Damage from accidents affecting the kidney-ureter junction.
Fibrosis – Abnormal tissue growth due to chronic irritation.
Signs & Symptoms
Persistent flank or abdominal pain.
Blood in urine (hematuria).
Recurrent urinary tract infections.
Nausea and vomiting.
Pain during urination.
Decreased urine output.
Palpable abdominal mass in severe swelling.
Fever with urinary infections.